Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death for people living with HIV, highlighting the pressing need for more integrated and people-centered services and improvements in TB case finding, treatment, and prevention.
As countries scale up differentiated service delivery (DSD) models, implications for TB programs must also be considered, including identifying best practices for screening for TB to improve TB case finding and integrating Tuberculosis Preventive Treatment in DSD models—making differentiated TB/HIV services a high priority for CQUIN countries.
Community of Practice

Launched in March 2019 following the CQUIN workshop in Lusaka, the community of practice (CoP) has focused on supporting the integration of TB-intensive case findings and TB preventive treatment (TPT) into less-intensive DSD models.
- Participants include 49 people from 11 network countries and global agencies/organizations, including OGAC, CDC, and WHO.
- Dr. Andrea Howard and Dr. Greet Vandebriel are the technical leads, supported by Ms. Matildah Chisanga (Regional Project Operations Coordinator).
Activities
- The first co-created product was a “differentiated TB/HIV” framework and toolkit designed to guide the integration of TPT into less-intensive DSD models.
- Toolkit (French)
- Toolkit (English)
- The CoP is now working with the Quality Management for DSD CoP to develop TPT integration standards and an assessment toolkit, which will be ready in the first quarter of 2024.
Resources
Archived Webinar: Recorded, June 1, 2023
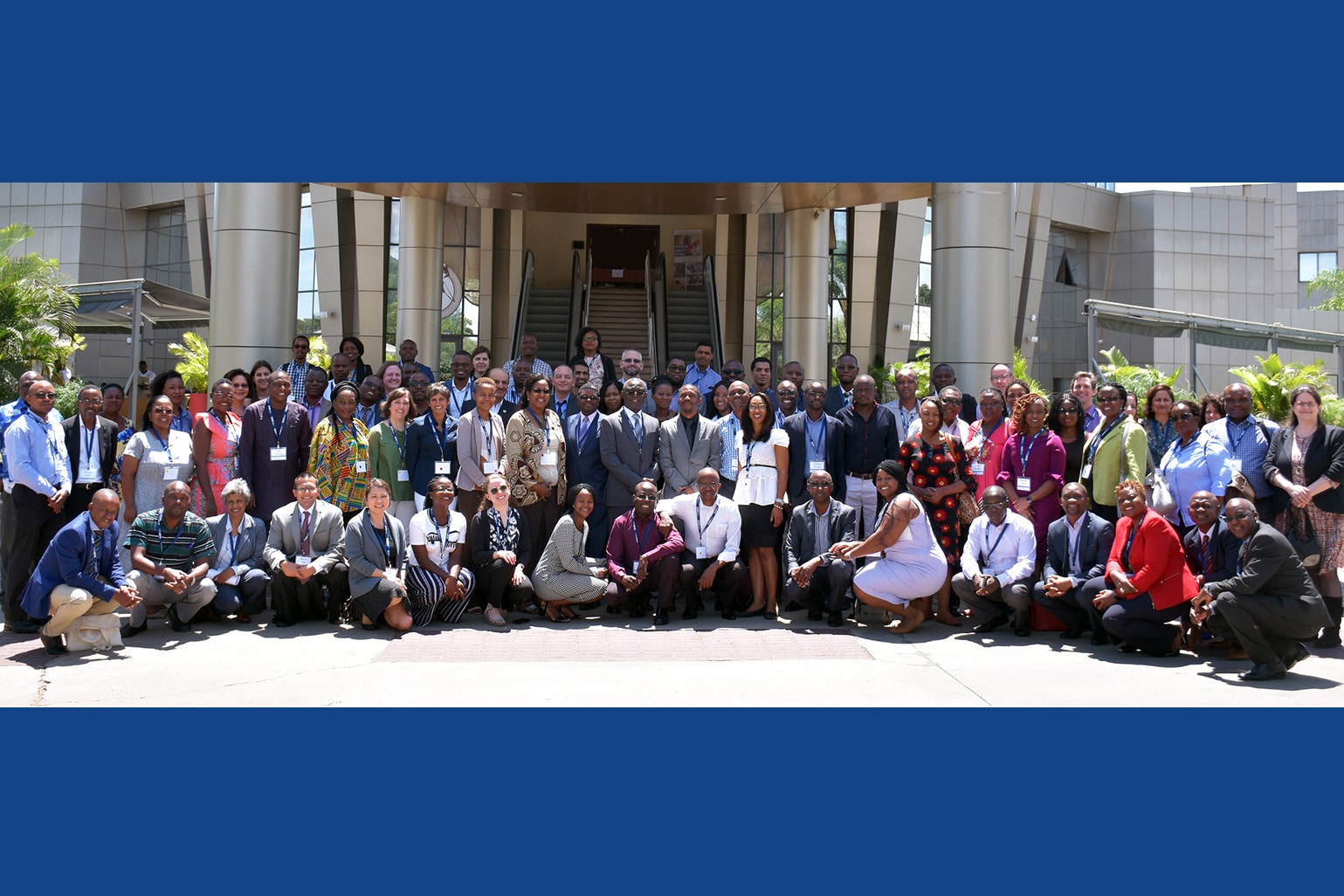

CQUIN Workshop: Opportunities and Challenges for TB Prevention and Care
CQUIN and the World Health Organization (WHO) hosted a seven-country workshop called “HIV Differentiated Service Delivery: Opportunities and Challenges for TB Prevention and Care” in Lusaka, Zambia from March 26-29, 2019. The workshop brought together over 120 global experts to explore the impact of differentiated HIV services on TB screening, diagnosis, prevention, and care; facilitate the exchange of relevant experiences, tools and best practices; and highlight innovations and new data.
Participants included representatives from ministries of health, civil society, academic institutions, and PEPFAR implementing partners from seven CQUIN countries, as well as global partners including WHO, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the International AIDS Society (IAS), the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), USAID, and the Global Fund.